B-SIM V2.5 Reference - Blow molding simulation

Tool
Tool in B-SIM is represented using a finite elements mesh. The tool representation is created directly in B-SIM using a simple dialog or the tool geometry can be imported from STL, DXF, Patran of VRML file. Once a tool is created, it can be scaled, rotated, translated, centered, mirrored and exported as DXF file. All these tasks are accessible from B-SIM Tool view.
- Tool creation / editing
- "ABR representation"
- Import from STL / DXF / Patran / VRML / HyperMesh ASCII
The tool representation can be created within B-SIM when using the built-in tool editor or imported from an external file (STL, DXF, Patran or VRML).
To create a new tool representation, click on the icon with the tool tip "New tool" on B-SIM shortcut bar or click on File / New and select B-SIM Tool as the document type and click OK.
The following dialog appears:
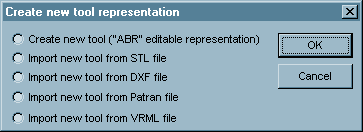
In this dialog box, select the way how the new tool will be created and click on OK. Depending on the selection, continue with Creating new tool using B-SIM ("ABR" editable representation) or Import from STL, DXF, Patran or VRML.
Creating new tool using "ABR" editable representation
B-SIM enables creating tools via series of 2-D contours, each representing a cross-section through the tool. The series of contours are stacked parallel to each other in the increasing Z-axis direction and are thus perpendicular to the Z-axis. The shape of a 2-D contour is defined by rectangle dimensions Ai, Bi and radius Ri (see below).
Two subsequent contours can have the same Z-coordinates; the program will automatically check for non-zero areas in the created tool faces. When entering the data points for the tool which is used as a mold, care should be taken to ensure that the face contained in the Z=0 plane should contain an opening to serve as the entry face through which a deforming parison / preform will enter the tool cavity. The last contour is automatically closed.
Meaning of contour parameters A, B, R:
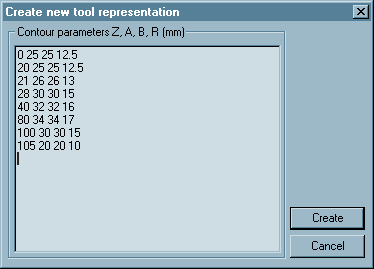
Click on File / New and select B-SIM Tool as the document type. Click OK. The following dialog appears:
 |
0 25 25 12.5 |
In the dialog box the following items have to be input:
- The Z-coordinate (mm or inch) of the first contour.
- The set of rectangle dimensions Ai (mm or inch) and Bi (mm or inch).
- The corner radius R (mm or inch).
Repeat the above procedure for the remaining contours. Click Save. The tool representation is automatically created and opened for further modifications:
Now, it is possible to click on Tool / Edit command and modify the entered tool parameters:
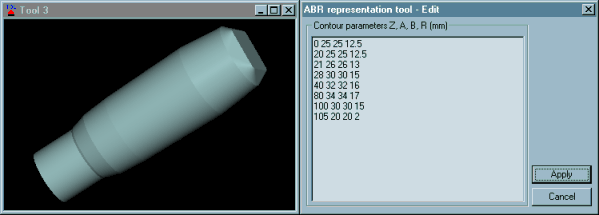
In this case, the radius of the latest contour was modified from 10 to 2 mm. Click on Apply to see the impact of the specified modification. It is possible to continue with modifications or to close the dialog. After closing, the modified tool can be saved using File / Save or File/ Save as command.
Every tool created using "ABR" editor remains editable until it is transformed, centered or mirrored. From this moment, the tool is no longer editable.
Creating new tool using import from STL / DXF / Patran / VRML
DXF Import
B-SIM translates only 3DFACE entity while importing data stored in DXF
file. So the DXF file must contain such entities to describe a tool
surface. Wire-frame model of a tool cannot be read by B-SIM. It is necessary
to create surface model.
STL (stereolithography)
Import
B-SIM can use tool representation which were created using CAD/CAM software
packages like SurfCam, CATIA, ProEngineer, CadKey etc. Usually, such
a 3D upper tool shape is more complicated than simple geometrical shape
which can be created directly using B-SIM built-in upper tool editor.
In case your CAD system for generating of 3D tools does not have STL
output, use a software converter from IGES or VDA-FS files to STL file.
There is an increasing number of such a software converters from one
type of the 3D representation to the STL files. (E.g. for PC : SurfCam,
MasterCam, CadKey ...)
B-SIM can handle directly stereolithographic (STL) format of the exported files for a tool. The STL files can be read by B-SIM when meeting following conditions:
- Stereolithographic (STL) file can be a text (ASCII) or binary file
- The polygons used must be triangles When using STL files, some
pitfalls may appear:
- The surface of the tool need not be covered continuously by triangles. If not, then tiny holes may arise. Then, during calculation some nodes of the parison / preform can penetrate through these holes and finally be in a position inside the tool. Of course, this is not acceptable. To avoid this situation, such holes must be patched by additional surfaces. The existence of holes in STL files is due to the process of conversion from complicated and often very curved NURBS surfaces to planar polygons of the STL. The quality of the conversion depends on the software used for this process. As a general rule, STL files created from 3D solid modelers, provide excellent surface without any holes.
- The geometrical position and orientation of the tool should fit the position and orientation of the parison / preform being blow molded. B-SIM does not check for this. It is user's responsibility to adjust the geometrical configuration of the parison / preform and the tool before the simulation starts. To make it easier, B-SIM offers command Tool / Center.
Patran Import This menu item enables import any tool shape saved in Patran format.
VRML Import Imports geometry from VRML file. Only VRML V2.0 is supported. Used mainly for simulation of Image pre-distortion using VRML files.
HyperMesh ASCII Import Imports geometry from HyperMesh ASCII file. Only *tria3 and *quad4 entities are recognized by the importing routine.
Transformations
To open a tool to transform - click on the icon with the tool tip "Open tool" and in Windows File Open dialog, browse for the tool file. Once the file is selected, click Open. A new window with the picture of the selected tool appears. Now, select command Tool / Move, Tool / Scale or Tool / Rotate to move, scale or rotate the selected tool.
Tool / Move:Moves the tool into a new position. The distance of the new position from original position is given by a vector with coordinates x, y, z. This command displays following dialog box:
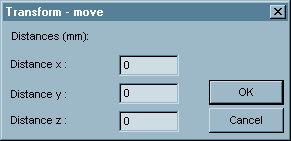
Enter the distances in direction of axis x, y and z.
Click OK to confirm the transformation. Click Cancel to cancel the dialog.
Tool / Scale:
Scaling of the tool in given direction. This command displays following dialog box:
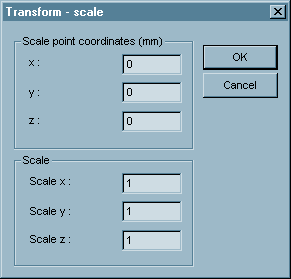
In Scale point enter coordinates of point to scale about.
In Scale enter scale in axis x, y and z.
Click OK to confirm the transformation. Click Cancel to cancel the dialog.
Tool / Rotate:
Rotate the tool around the given axis with given angle of rotation.
This command displays following dialog box:
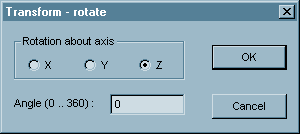
Select the axis about which the rotation should be performed.
Enter the angle of rotation.
Click OK to confirm the transformation. Click Cancel to cancel the dialog.
Centering, mirroring
To open a tool to center or mirror - click on the icon with the tool tip "Open tool" and in Windows File Open dialog, browse for the tool file. Once the file is selected, click Open. A new window with the picture of the selected tool appears.
To center the tool, click on Tool / Center command. A message box saying "Move tool center [x,y] to [0,0] ?" appears on the screen. Click Yes to center the tool. After centering, the tool should be save using command File / Save or File / Save as.
To mirror the tool, click on Tool / Mirror(x) command. The tool will be automatically mirrored using a mirror plane x = (tool x min), where (tool x min) is the minimal x tool coordinate. After mirroring, the tool should be save using command File / Save or File / Save as.
Centering, mirroring
To open a tool to center or mirror - click on the icon with the tool tip "Open tool" and in Windows File Open dialog, browse for the tool file. Once the file is selected, click Open. A new window with the picture of the selected tool appears.
To center the tool, click on Tool / Center command. A message box saying "Move tool center [x,y] to [0,0] ?" appears on the screen. Click Yes to center the tool. After centering, the tool should be save using command File / Save or File / Save as.To mirror the tool, click on Tool / Mirror(x) command. The tool will be automatically mirrored using a mirror plane x = (tool x min), where (tool x min) is the minimal x tool coordinate. After mirroring, the tool should be save using command File / Save or File / Save as.
Sometimes, some areas of a tool are not needed for the
simulation or these areas cause improper results, not corresponding
to the reality. In such a case, it is possible to remove faces from
tool. Cut tool command from Tool menu displays Cut tool (remove
faces) dialog:
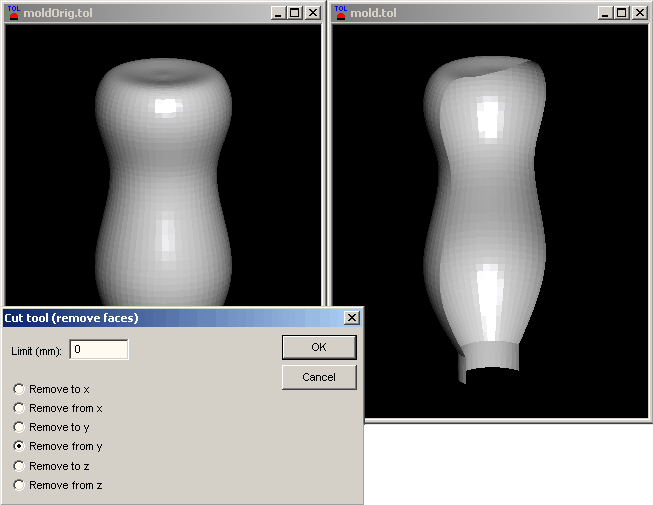
The figure above shows original tool on the right and modified tool on the left. Cut tool dialog shows the data used for faces removal. In this particular case, faces (triangles) with all nodal coordinates y greater than 0 (limit) were removed. Other faces were cut (in case they cross the dividing plane) or left unchanged (in case they do not interfere with the dividing plane).
Export as DXF
Every tool can be exported in DXF format. To open a tool
for export, click on the icon with the tool tip "Open tool"
and in Windows File Open dialog, browse for the tool file. Once the
file is selected, click Open. A new window with the picture of the selected
tool appears. Now, click on Tool / DXF export.
In Windows File Save As dialog, specify a DXF file name and click Save.
The DXF representation of the B-SIM tool will be created.
B-SIM Tool view
B-SIM Tool view is a window enabling to display and perform modifications of tools A tool is displayed in B-SIM Grid view after creation or after opening:
To open the tool - click on the icon with the tool tip "Open tool" and in Windows File Open dialog, browse for the tool file. Once the file is selected, click Open. A new window with the picture of the selected tool appears:

B-SIM Tool view allows to:
- Rotate, zoom and pan the displayed tool
- Transform the tool
- Center and mirror the tool
- Export the tool as DXF
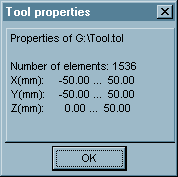
- Display properties of the tool - click on Tool / Properties. The following dialog appears with general information about the open tool: